Bamboo Material
What is Bamboo?
Bamboo, a rapidly renewable rhizomal grass, is one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth, with some species growing up to 60 feet in just a few months. This exceptional growth rate makes bamboo an eco-friendly material, ideal for various construction and manufacturing applications. Its ability to regrow naturally without the need for replanting or irrigation contributes to its sustainability, making it a popular choice for eco-conscious projects.
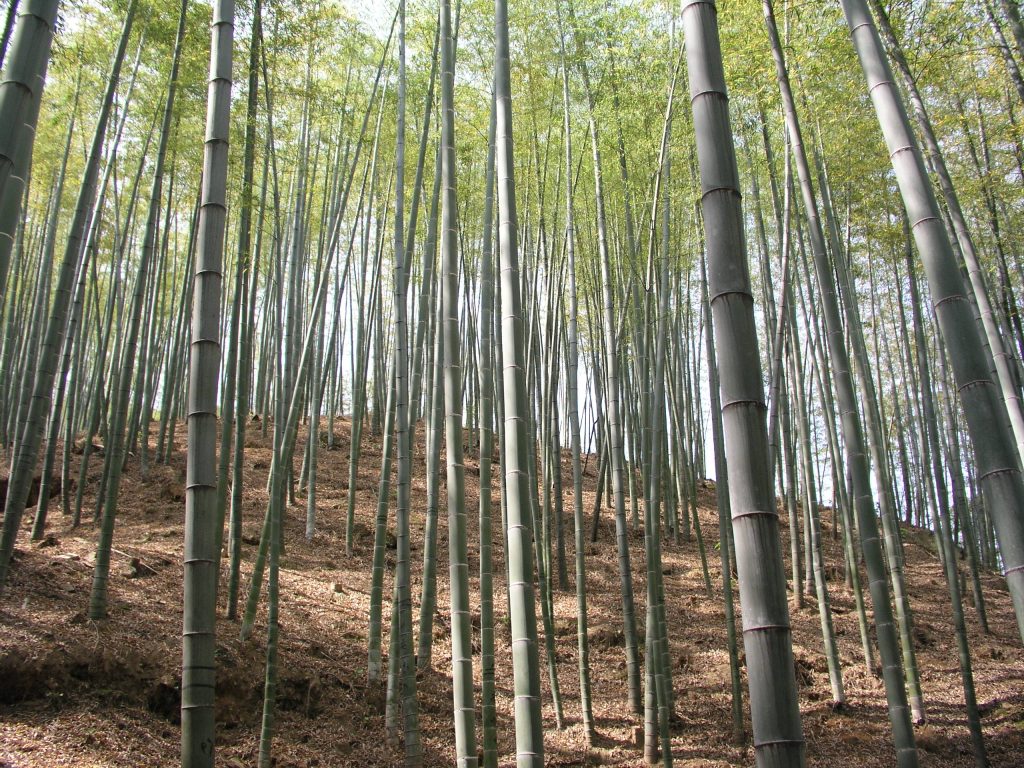
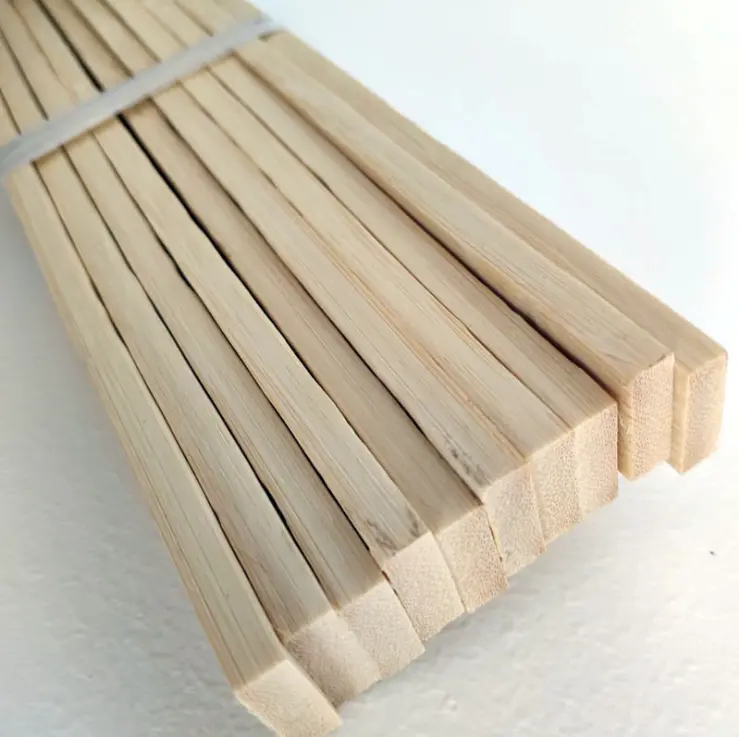


Bamboo's Growth and Harvesting
Bamboo’s growth cycle varies depending on climate and region but typically requires 5-6 years to reach maturity. It’s harvested during this period to ensure the fibers are at their hardest and most suitable for use in construction. The harvesting process involves cutting bamboo poles, which are then dried, split into strips, and de-skinned before being processed into building materials like beams, panels, and flooring.
Manufacturing Process
Once harvested, bamboo undergoes several stages to become construction-ready:

1. Drying and Splitting
Bamboo poles are dried and cut into strips. These strips are de-skinned and planed to ensure uniformity and durability.
2. Laminating
The bamboo strips are laminated together using low-VOC or inert adhesives, ensuring the finished product is safe and durable. This process also impacts the environmental footprint, as certain glues used in laminating can release harmful toxins like formaldehyde.
3. Finishing
Bamboo is sanded and further dried to achieve optimal moisture content, which is essential for stability, especially in varying climate conditions. Finishes are applied depending on the product’s use, such as food-safe oils for kitchen products or urethanes for high-wear applications.
Benefits of Bamboo
Bamboo offers numerous benefits to the ecosystem:
- Low Environmental Impact: Bamboo grows without fertilizers, pesticides, or irrigation and helps stabilize soil, preventing erosion. Its rapid regrowth also means there’s minimal disruption to the land.
- Carbon Sequestration: Bamboo forests sequester a significant amount of CO2, with some species able to store 5-40+ tons of CO2 per hectare annually. This makes bamboo an excellent material for carbon offsetting and long-term environmental sustainability.
- Biodegradability: Unlike synthetic materials, bamboo decomposes healthily, making it a safer alternative for the environment at the end of its life cycle.
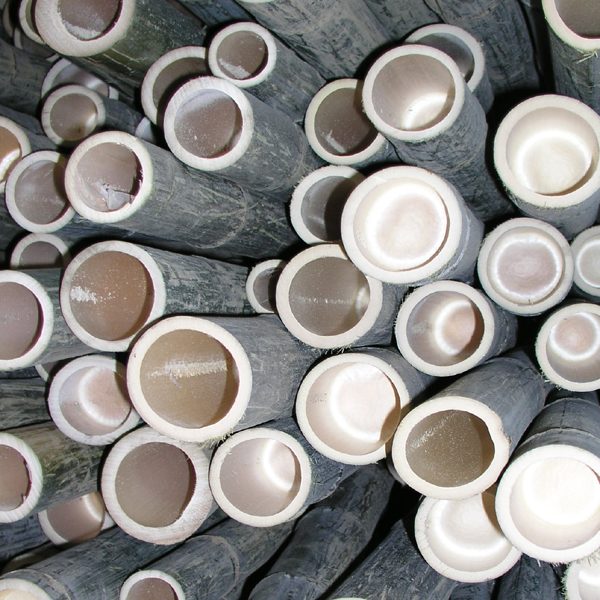


Strandwoven Bamboo: Durability and Stability
Strandwoven bamboo is one of the most durable forms of bamboo used in construction. It’s ideal for high-traffic commercial applications due to its:
- Hardness and Density: With a Janka hardness rating of over 3200, Strandwoven bamboo is significantly harder than traditional hardwoods.
- Stability: The lamination process used in Strandwoven bamboo results in unmatched dimensional stability, making it an excellent choice for floors in areas with varying humidity levels.
- Aesthetic Options: Available in natural, carbonized, or custom-stained finishes, Strandwoven bamboo can be tailored to any design specification.

Environmental and Economic Advantages
Bamboo is a highly efficient material for both production and carbon sequestration. With its circularity, bamboo can be fully utilized in products ranging from food and textiles to paper and construction materials. Its use reduces waste and promotes sustainable economies. The growing demand for bamboo-based products, such as flooring, panels, and engineered bamboo materials, has bolstered the bamboo industry, especially in China, which is the largest producer and exporter of bamboo products.
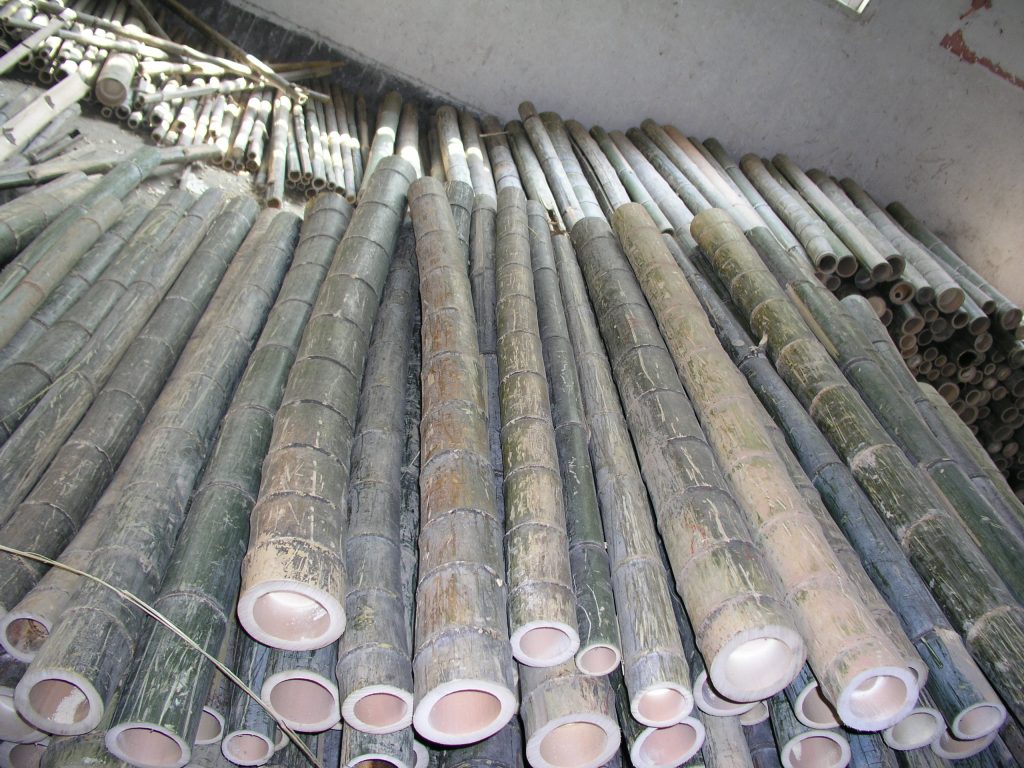

Applications in Modern Construction
Bamboo is increasingly used in the construction of eco-friendly buildings, including bamboo structural lumber for roofs and poles. It is also used in solar energy houses, where bamboo culms are combined with solar energy technology to reduce the building’s energy consumption.
Conclusion
Bamboo, as a construction material, offers exceptional sustainability, durability, and environmental benefits. Whether used for flooring, panels, or structural components, bamboo is a material that not only supports the environment but also provides strong, reliable products for modern construction. By choosing bamboo, developers and manufacturers can contribute to a circular economy while benefitting from a durable, cost-effective material.
Join our Community of Designers and Architects
Register below for your Trade Account and get your samples for free.